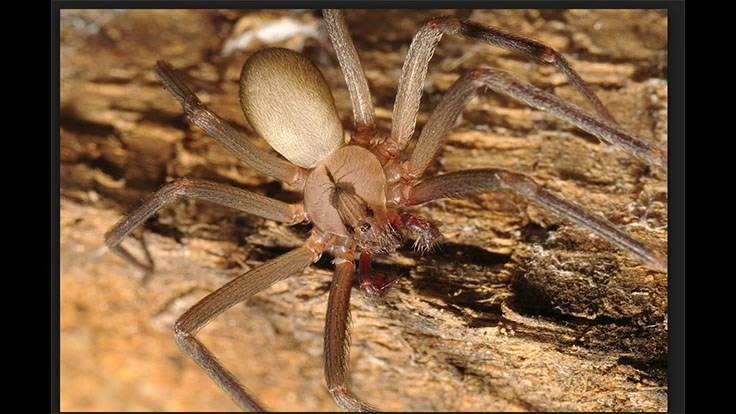
A spider's sticky web contains traces of the critter's DNA, as well as the DNA of whatever prey that was unlucky enough to get stuck in the web, according to a new study, which found that these tiny samples of DNA can be amplified and sequenced in a lab. In other words, an empty spider web isn't a mystery; it's a clue that can tell scientists what kind of spider built the web and what prey it snagged in its trap.
Knowing exactly which species of spider built a web in a certain area, as well as knowing what that spider feasted on, is important information for researchers in a variety of fields -- from conservation ecology to pest management, said study lead author Charles C.Y. Xu, a graduate student in the Erasmus Mundus Master Programme (MEME) in evolutionary biology, a joint program hosted by four European universities and Harvard University in the United States.
Click here to read the entire article.
Source: CBS News
Latest from Pest Control Technology
- Earn CEUs from Your State at Next Week’s Mosquito Control Virtual Conference
- Preserving Culture, Providing Opportunities Key in Hoffman’s Decision
- Winter Weather Could Decide How Bad Mosquito Season Gets
- Trent Frazer Discusses How Mosquitoes Survive Winter
- Barnes Exterminating Acquires Tennessee Pest Solutions
- Pest Index Up 9% YOY in January
- Arrow Exterminators Acquires Hoffman's Exterminating
- PMPs Plan Mera Peak Summit for Parkinson's