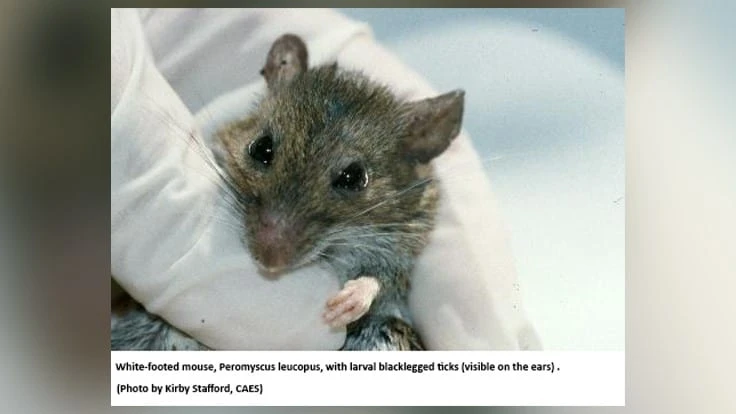
“Along with fewer infected mice, we observed a second effect also seen in previous laboratory-based studies,” notes Scott Williams, PhD, Agricultural Scientist at the CAES and a co-author of the study. “The vaccine causes the generation of antibodies in the mice. Previously infected ticks will ingest those antibodies when feeding on mice and be ‘cleared’ of infection. So, feeding ticks are a ‘xenodiagnostic marker’ of vaccine impact.” According to Williams, when non-infected mice consume vaccine-coated pellets, they are protected from infection with Borrelia burgdorferi. “Non-infected ticks, therefore, cannot pass the disease to other animals, including humans” he says.
The vaccine is currently undergoing the USDA regulatory process for commercial licensure. The research program was supported, in part, by U.S. Hatch Act funds, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CK000182-03), and US Biologic.
Latest from Pest Control Technology
- Earn CEUs from Your State at Next Week’s Mosquito Control Virtual Conference
- Preserving Culture, Providing Opportunities Key in Hoffman’s Decision
- Winter Weather Could Decide How Bad Mosquito Season Gets
- Trent Frazer Discusses How Mosquitoes Survive Winter
- Barnes Exterminating Acquires Tennessee Pest Solutions
- Pest Index Up 9% YOY in January
- Arrow Exterminators Acquires Hoffman's Exterminating
- PMPs Plan Mera Peak Summit for Parkinson's