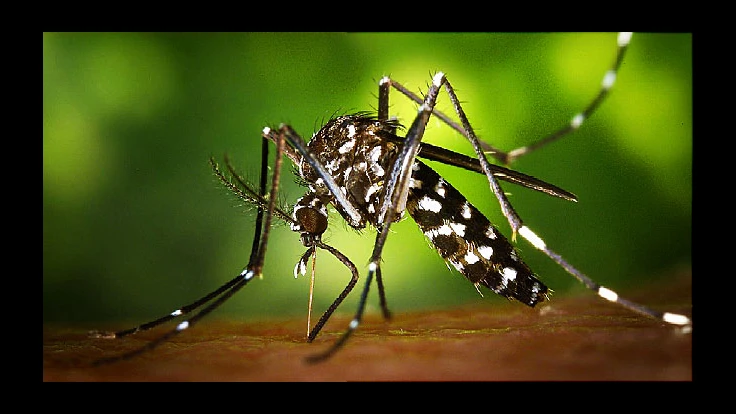
For the first time in the Western Hemisphere, researchers have detected the Zika virus in Aedes albopictus, the mosquito species known as the “Asian tiger,” a finding that increases the number of U.S. states potentially at risk for transmission of the disease, the Washington Post reported.
During the summer months when U.S. mosquito populations are at their peak, albopictus are more ubiquitous than the Aedes aegypti that have been the primary vector of the spread of Zika elsewhere in the Americas. Unlike the aegypti mosquito, which is mostly present in southern United States and along the Gulf Coast, the albopictus has a range as far north as New England and the lower Great Lakes.
The discovery was reported recently by the Pan American Health Organization after researchers in Mexico confirmed the presence of Zika in Asian tiger mosquitoes captured in the state of San Luis Potosi and sent them to government labs for testing.
Click here to read the entire article.
Source: Washington Post
Latest from Pest Control Technology
- Earn CEUs from Your State at Next Week’s Mosquito Control Virtual Conference
- Preserving Culture, Providing Opportunities Key in Hoffman’s Decision
- Winter Weather Could Decide How Bad Mosquito Season Gets
- Trent Frazer Discusses How Mosquitoes Survive Winter
- Barnes Exterminating Acquires Tennessee Pest Solutions
- Pest Index Up 9% YOY in January
- Arrow Exterminators Acquires Hoffman's Exterminating
- PMPs Plan Mera Peak Summit for Parkinson's